Gepubliceerd in: Clinical Biomechanics 2019 (65):92-99

In vitro assessment of connection strength and stability of internal implant-abutment connections
Lees hieronder de samenvatting van de Friction-fit versus Conical seal.
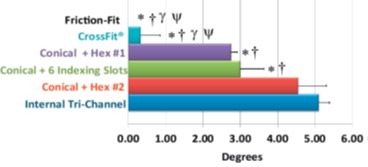
Abutment Rotation:
What it is: Abutment rotation measures the degree of abutment rotation possible after the abutment screw is torqued to the manufacturer’s recommendation, then removed.
Why it’s important: During occlusal loading, any abutment rotation creates tension in the screw connection, contributing to screw loosening, screw joint failure, and prosthetic failure. Without this abutment rotation the Friction-Fit Connection may have a lower risk of screw-loosening and failure than conical connections.
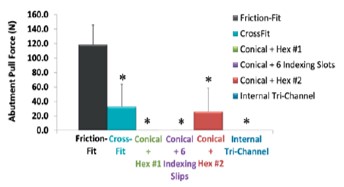
Abutment Pull Force
What it is: Abutment pull force measures the force required to separate the abutment and implant after the abutment screw is torqued to the manufacturer’s recommendation, then removed.
Why it’s important: The abutment pull force indicates the amount of frictional contact and stability between components. With significant contact between the implant and abutment, the Friction-Fit Connection has a lower risk of instability and movement than the conical connections tested.
Abutment Micromotion
What it is: Abutment micromotion is horizontal abutment movement under dynamic loading.
Why it’s important: Measurements of micromovement indicate the presence of a microgap between components. A microgap presents a potential area for bacterial infiltration and colonization, which may contribute to peri-implant disease. In addition, microgaps may be a factor in prosthetic instability, potentially resulting in overload and bone loss.
.jpg)
Meer info op:https://www.clinbiomech.com/article/S0268-0033(18)30967-7/fulltext